
Oracle EBS Mobile Apps
Content
As an Oracle E-Business Suite (EBS) user, you can access key functionalities directly from your mobile phone or tablet with Oracle’s Mobile Applications.
Approving annual leave requests, entering your expenses, raising a purchase order, moving stock around the warehouse and stock counting are all available to you, whether you are working from home or out of the office.



Among DSP's customers, the most popular apps are Mobile Approvals, Expenses, Procurement and Supply Chain. However, the full range of mobile apps covers featured in:
-
Order Management
-
Oracle HCM
-
OTL
-
Projects
-
Field Service
-
Learning Management
-
Asset Management
-
Inventory
My Oracle Support note 1641772.1 contains the full list of available apps plus some handy links to related documentation.
Most of the applications focus on a particular feature (e.g. raising a Sales Order) or group of closely related features (e.g. Stock Counting and stock enquiries in Mobile Supply Chain). The main exception is the Mobile Approvals application which spans all modules which use Workflow approvals.
Oracle’s mobile applications have been around for some time, but continue to be modified and updated with more EBS functions being made available on mobile platforms. The apps are free to download from either Google Play or the Apple App Store. Users must be licensed for the base products, with mobile services configured on the Oracle EBS server. For example, to use Mobile Expenses you will need to be licensed for the Payables module. To find Oracle EBS mobile apps, search for the keywords "Oracle America Inc." in the Apple App Store and Google Play.
One of the particular advantages of these apps is their ease of use. Assuming that users are familiar with the back-end Oracle functions, such as entering an expense claim, then there is no training required on the apps. They are easy to download from the Apple or Google stores and with a bit of basic setup (just a URL in most cases) you can start immediately.
Some examples of the mobile apps are shown below. As you can see from the screen-shots the screens have been intentionally left simple, uncluttered and focused on the task at hand. This design also reduces the load on the mobile device as well as the communications load with the server.
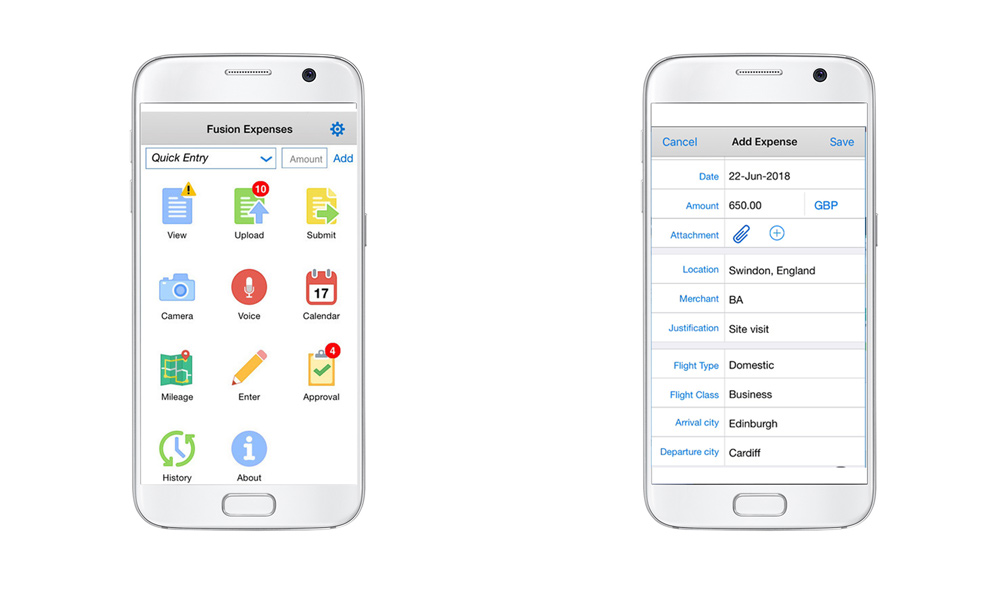
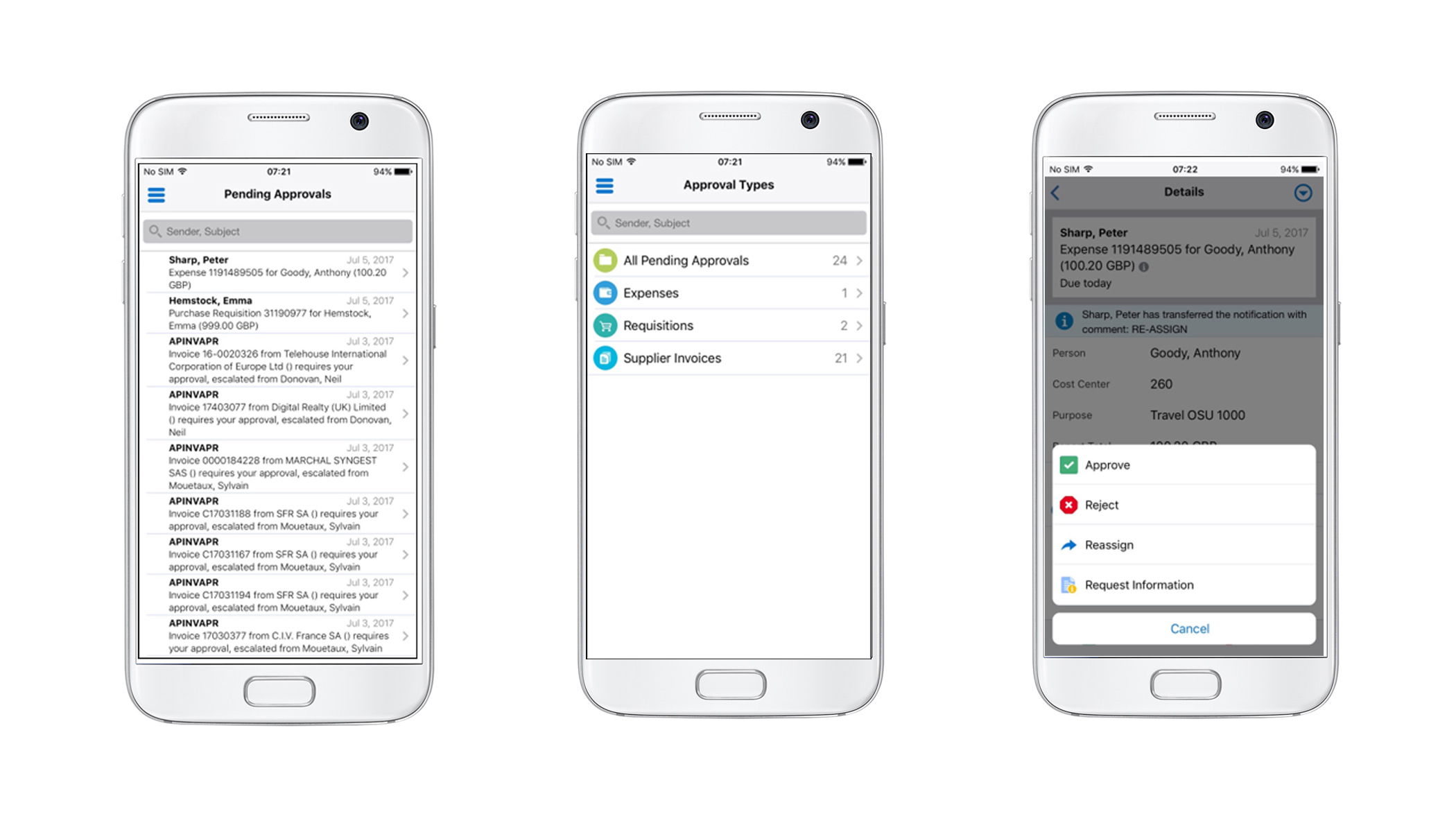
EBS mobile apps are built using Oracle’s Mobile Application Framework (MAF). This is the same framework that customers can use to build their own apps if none of the standard offerings meet their needs. Please note however that Oracle does not support customisation of the mobile app code in the standard mobile apps beyond some corporate branding options and the usual flexfield extensions.
As you can see from the diagram below the apps communicate with EBS using REST webservices. The required REST services are deployed in EBS as part of the standard Mobile Framework. Beyond some patching on pre-12.2.10 installations, the REST services should be ready for use.
From the security standpoint users will use their existing EBS username and password to authenticate themselves (no separate account details to remember thankfully). The default (out of the box) security model is the basic username and password variety although other options including single sign-on are available and Claremont has experience implementing these models.
The following diagram illustrates the high-level technical architecture overview for Oracle EBS mobile apps:
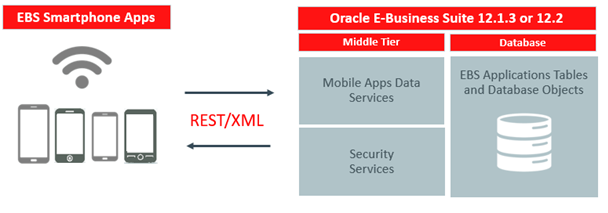
Oracle EBS mobile apps are compatible with both Release 12.1.3 and Release 12.2.3 and onwards, as well as iOS 12.3 or later and Android 6.0 or later. EBS mobile apps are available only on the Apple iOS and Google Android platforms.
It is worth noting that there are some minor differences in behaviour when comparing the apps on iOS and Android. When developing these applications Oracle will test the iOS versions on iPhones, iPod Touches and iPads which gives very good device coverage. On the Android platform, Oracle will test on Samsung Galaxy and Google Nexus devices only. Due to the huge variety of Android handsets available, Oracle does not provide device-specific certifications on this platform.
As shown in the earlier diagram, there is no new technology required on the Oracle EBS server for the mobile apps. To use the Oracle EBS mobile apps, you only need to apply server-side patches and perform some setup tasks to configure your mobile app on the server.
One of the most important questions customers need to answer is how to securely connect their mobile apps to EBS without compromising network security. Fortunately, there are a number of ways of doing this as you can see in the below diagram.
All of the options described in this diagram are supported by Oracle as methods of connecting mobile apps to EBS. The key point with any of these options is that the mobile app is able to reach the REST web service end-point in order to carry out authentication and transactions.
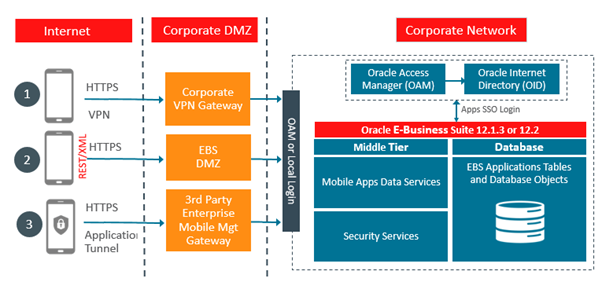
1. Using a Virtual Private Network
The use of a VPN avoids the need to run EBS in a DMZ (De-Militarised Zone) configuration. However, it does mean that users will have to sign in to the corporate VPN before they sign in to the mobile app. It also necessitates a separate install of VPN software on the mobile device. The type and version of VPN software would generally be controlled centrally.
2. Using a DMZ
To access the Oracle E-Business Suite mobile apps over the Internet, your Oracle E-Business Suite environment must be set up in a DMZ configuration. For additional information on performing this configuration, see Advanced Configurations for Demilitarized Zone (Mobile Applications Administrators Guide). If your Oracle E-Business Suite environment is not set up in a DMZ configuration, mobile app users must access the Oracle E-Business Suite mobile apps through an intranet connection, such as a virtual private network (VPN) see above.
3. Through Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) Solutions
Oracle EBS mobile apps developed using Oracle Mobile Application Framework (MAF) can integrate with third-party Enterprise Mobility Management solutions that support common AppConfig standards, such as VMware AirWatch.
The key point to a success architecture is to preserve the security and integrity of your EBS application. The DMZ, reverse proxy servers, firewalls and certificates are common ways that organisations employ to protect themselves. Oracle mobile applications support a number of different architectural models which allow secure communications (see My Oracle Support and the Mobile Apps Administrators Guide for assistance).

Oracle’s mobile applications have been developed under the Mobile Applications Framework (MAF), allowing users to develop their own mobile applications in the event that one of the standard applications doesn’t deliver all the functions needed.
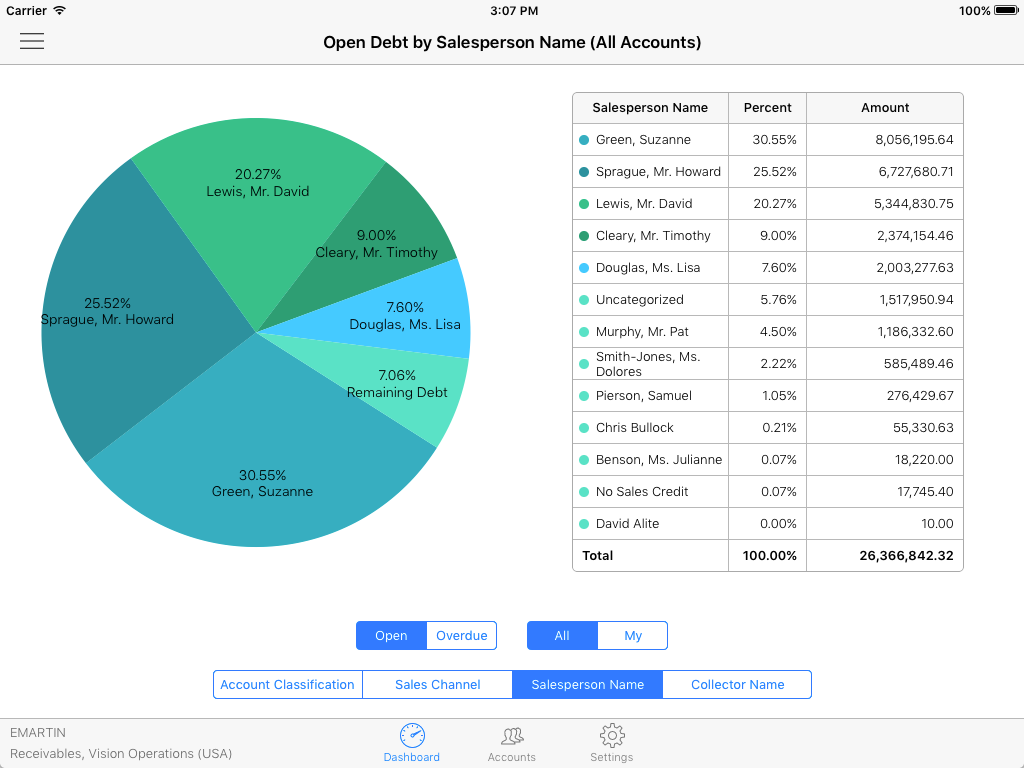
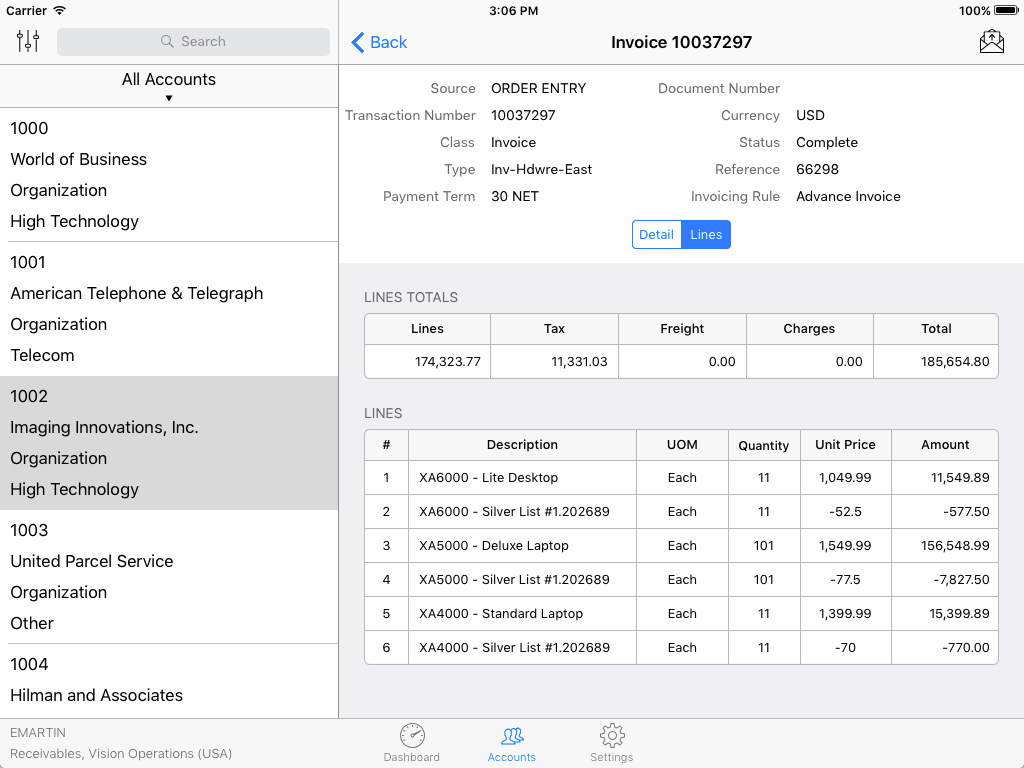
Below are some examples of custom mobile applications built by Claremont’s (now DSP) development partner, Kogitas.
These include receivables debt, invoice details, concurrent program, and workflow status information.

Contact us Today
Want to discuss our Oracle EBS Managed Services with an Oracle Account Director? Or maybe you'd like to schedule a reference call with one of our current managed service customers? Fill out the form below and we'll be in touch shortly!


.png?width=250&height=56&name=stonewater-logo%20(1).png)


